Architecture – Netscan
Introduction
Almaden NetScan is a plug-in for the ADA Module that can search for active IP addresses and retrieve configuration data from them. This data is periodically collected and automatically, along with other samples from ADA.
One of the most important features of NetScan is determining the exact number of machines in your company’s network. It scans the network and provides the total number of machines within the company’s network and identifies which machines do not yet have the Desktop or Server agent installed.
Prerequisites
- ADA must be installed for the product to function.
- You must have System Administrator privileges on the applicable operating systems.
- The host must be powered on at least once within the defined period to search for active IP addresses. You will need to select the IP address range(s) for the scan.
Topology
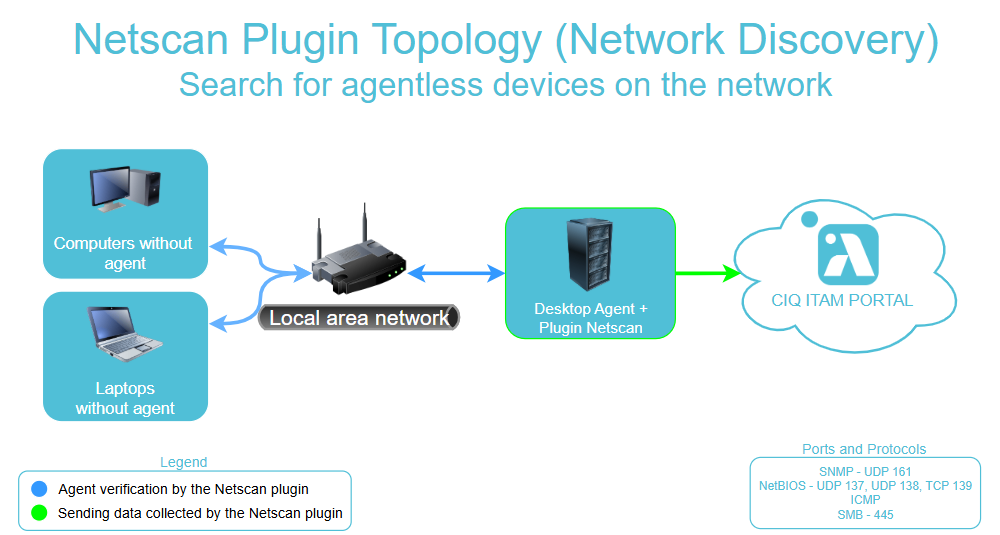
Additional Configuration Options
- “Desktop/Server”: You must choose one of these options to classify all machines within the scanned IP range as either “Desktops” or “Servers.” The default option is “Desktop.” After selecting this, you can edit it later . This may transfer backlog from desktop to server. A confirmation message will be displayed before proceeding.
- “Ping each IP before scanning”: When enabled, this option ensures that the NetScan plug-in contacts each IP address before scanning it for configuration data. If the contact attempt fails, the machine will not be scanned.
- “Include non-Windows Machines”: Enable this option if you want to scan for non-Windows machines as well. Any type of machine (Unix/Linux) can be detected, provided that Samba Server is correctly installed and configured. This option is only available when “Ping each IP before scanning” is selected.
Data Collection Process
The NetScan plugin uses multiple protocols to map and identify devices on the network, correlating information such as IP address, hostname, domain, and additional characteristics.
Protocols and Methods Used
ICMP (Ping)
- Purpose: Discover which IP addresses are active.
- Operation: Sends ICMP Echo Request packets; the response confirms the availability of the host.
SMB (Server Message Block) / NetBIOS (Port 445)
- Purpose: Retrieve Hostname, NetBIOS Name, and Domain/Workgroup.
- Operation:
- During the SMB handshake (versions v1, v2, and v3), the client may obtain host identification information.
- The NetBIOS Node Status Response can, in some scenarios, also provide the device’s MAC Address, without relying on ARP.
- Collected information:
- Computer name (NetBIOS/Hostname)
- Domain or Workgroup
- In some cases, the MAC Address
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) (Port 161)
- Purpose: Query data from network devices (printers, switches, routers, etc.).
- Operation:
- Reads OIDs (Object Identifiers) from active SNMP agents (UDP port 161).
- Returns administrative data such as manufacturer, model, firmware version, serial number, etc.
🔹 Extracted Information
| Information | Protocol Used |
|---|---|
| IP Address | ICMP / predefined |
| Hostname / NetBIOS | SMB |
| Domain/Workgroup | SMB |
| MAC Address | SMB (in some cases) |
| Device data | SNMP |
What to Do When a Device Is Not Found by NetScan
If NetScan does not identify a device, follow the steps below to verify connectivity and network services:
1. Check if the device responds to Ping (ICMP)
Command:
ping <HOST_IP>- ✅ Reply received → The device is active on the network.
- ❌ No reply → The device may be powered off, disconnected, or ICMP might be blocked.
2. Test SMB communication (port 445)
Windows (CMD/PowerShell):
net view \\<HOST_IP>or
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName <HOST_IP> -Port 445Linux:
smbclient -L //<HOST_IP> -N- ✅ Returns shares / host information → SMB is active.
- ❌ Connection error → The SMB service may be disabled, blocked by a firewall, or inaccessible.
3. Verify if SNMP is enabled (for printers, switches, routers, etc.)
Linux:
snmpwalk -v2c -c public <HOST_IP>Windows (with SNMP tools installed):
snmpwalk.exe -v2c -c public <HOST_IP>- ✅ List of OIDs returned → SNMP is active.
- ❌ Timeout / no response → SNMP may be disabled, the community string is incorrect, or UDP/161 is blocked.
4. Additional Checklist
- Is the IP address correct?
- Is the device on the same network or accessible via routing/firewall?
- Does the host’s firewall allow ICMP, SMB, and/or SNMP?
- Are the network services (SMB/SNMP) enabled and properly configured on the device?
Summary:
- If the device does not respond to Ping, it is likely offline or blocked.
- If it responds to Ping but not to SMB, there may be a firewall restriction or the service is disabled.
- If it is a network device and does not respond to SNMP, check if SNMP is enabled and correctly configured.

