Device Calculation Structure
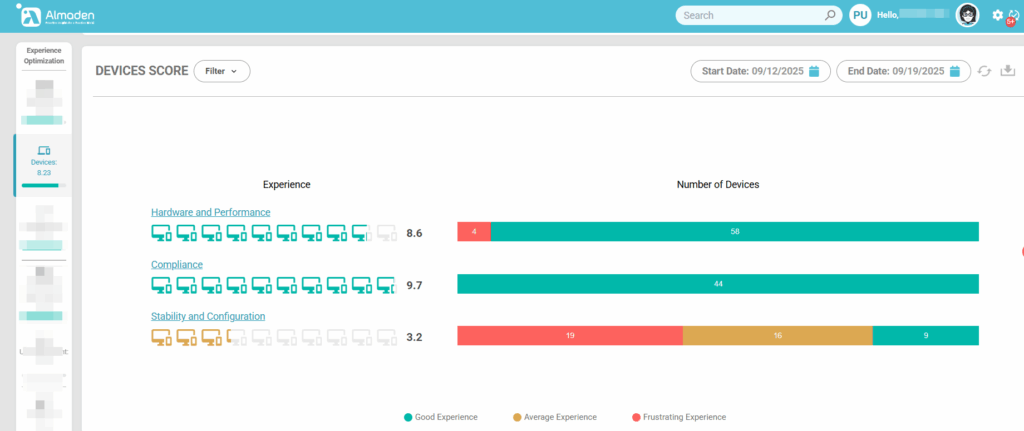
The calculation for Devices is divided into three main groups:
- Hardware and Performance
- Evaluates how well the device’s physical resources (CPU, memory, disk, startup time, and device age) support user productivity.
- Compliance
- Ensures the device follows organizational standards, including valid licensing, updated operating systems, and the presence of only approved software.
- Stability and Configuration
- Measures the reliability of the system by analyzing event errors and WMI health, indicating whether the device is stable and properly configured.
Together, these groups provide a balanced view of both the technical health and policy compliance of each device, resulting in an accurate experience score.
Each group has specific metrics that contribute to the device’s score.
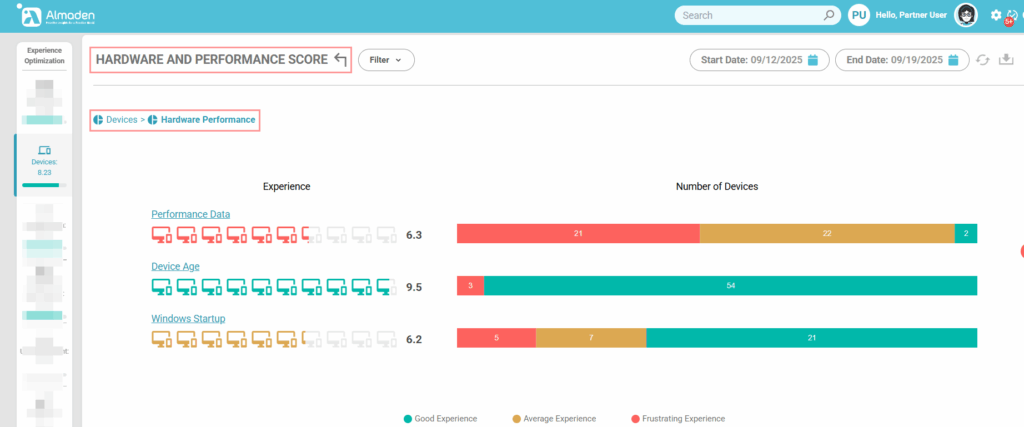
1. Hardware and Performance
This group measures the physical capacity and operational performance of the device. It considers key metrics such as CPU, physical and virtual memory, disk usage, device age, and Windows startup time. These indicators show how efficiently the hardware supports day-to-day tasks and how performance issues may impact the user experience.
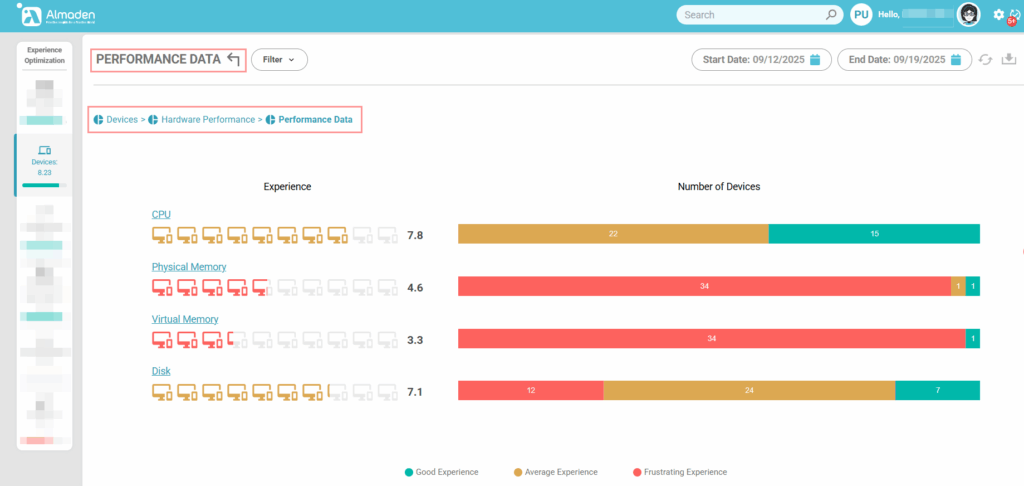
1.1 Performance Data
The score is based on the weighted average of the following indicators:
- CPU Usage (%)
- Example: A device with average CPU usage > 85% during work hours typically receives a score of ≤ 4.
- Physical Memory (RAM)
- Example: A laptop with only 4 GB RAM running multiple applications will score low.
- Virtual Memory (Swap/Pagefile)
- Example: Excessive paging activity lowers the score.
- Disk Performance (IOPS/Latency)
- Example: An HDD with high latency will score lower than an NVMe SSD.
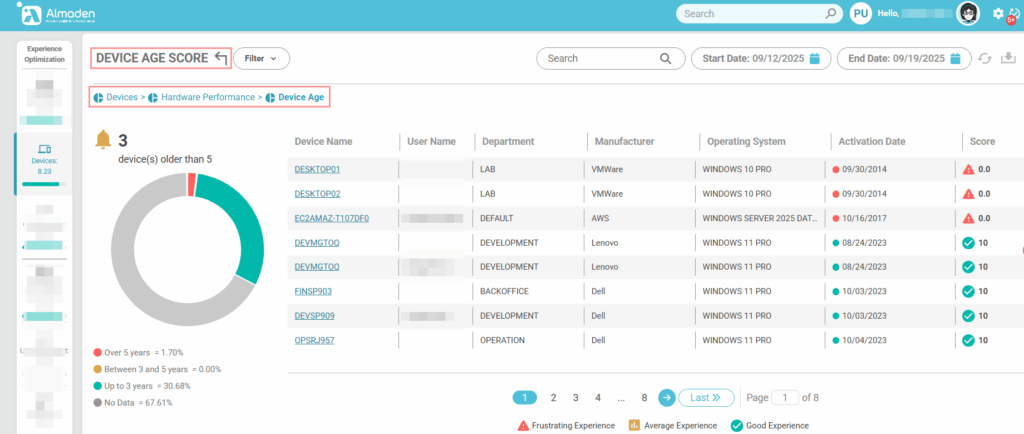
1.2 Device Age
Measures the age of the equipment, considering the time since its purchase or initial deployment. Older devices typically face greater risks of reduced performance, hardware failures, and compatibility issues. As the device ages, the score decreases, reflecting its diminishing capacity to deliver a smooth and reliable user experience.
This information is based on the BIOS Activation date reported by the device’s motherboard:
1.3 Windows Startup
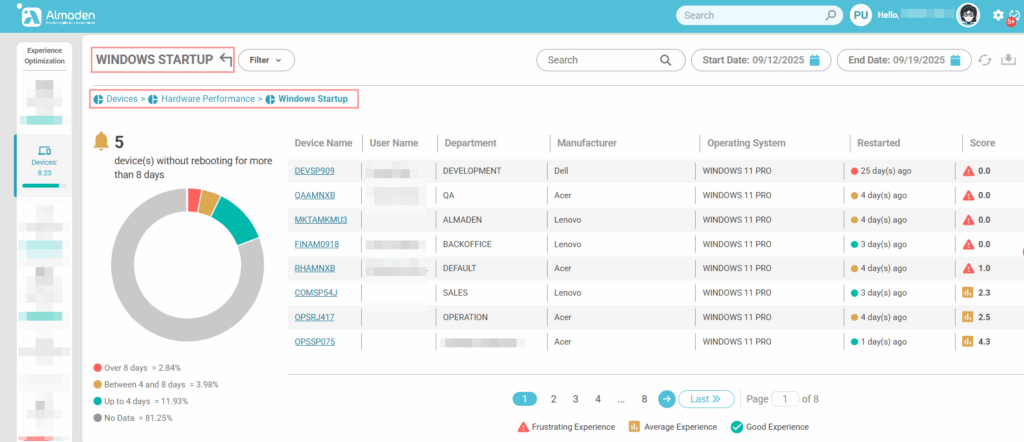
Measures the time required for Windows to complete the boot process and become fully operational. Longer startup times often indicate underlying issues such as excessive startup applications, hardware limitations, or configuration problems. A higher score reflects faster boot performance, contributing to a more efficient and responsive user experience.
Boot time:
- < 30 seconds: score 10
- 30–60 seconds: score between 6 and 8
- 60 seconds: score ≤ 5
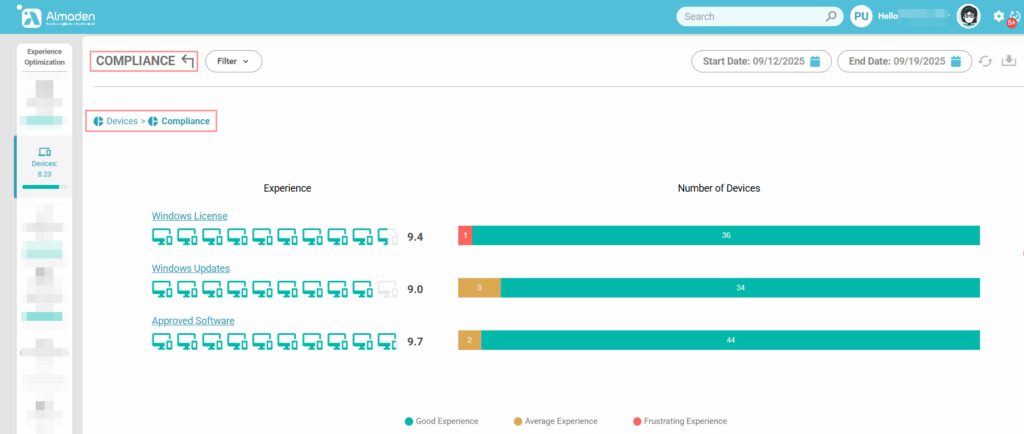
2. Compliance
Evaluates whether the device is aligned with organizational compliance policies. This group verifies critical aspects such as Windows licensing status, the application of security and feature updates, and the presence of only approved software. A higher score indicates that the device meets corporate standards, reducing risks related to security, legal exposure, and operational inconsistency:
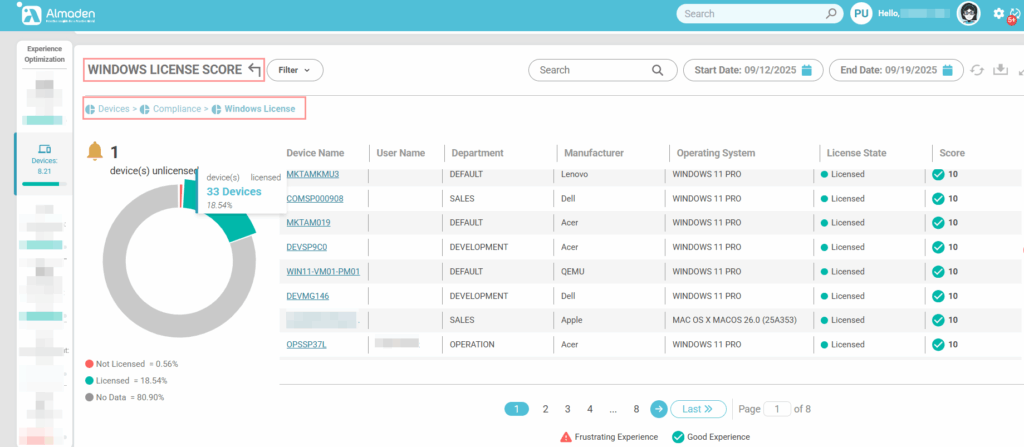
2.1 Windows License
Validates whether the device is properly licensed. A valid and active Windows license ensures compliance with legal and organizational requirements, resulting in the maximum score (10). If the license is invalid or expired, the device receives the minimum score (1), reflecting a critical compliance issue that must be addressed immediately:
- Properly licensed: score 10
- Invalid or expired license: score 0
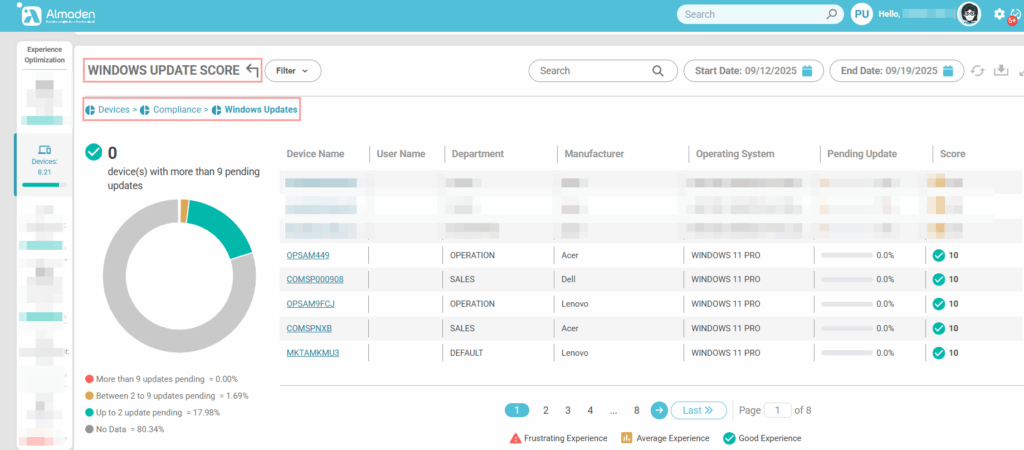
2.2 Operating System Update Score
Assesses whether the device has the latest Windows updates installed. A fully updated system, with all security patches and feature updates applied, receives the maximum score (10). Devices with critical pending updates receive a reduced score (≤ 4), highlighting potential security vulnerabilities and compliance risks that must be remediated promptly.
- Fully updated (latest patches installed): score 10
- Critical pending updates: score ≤ 4
2.3 Approved Software
Evaluates whether only organization-approved software is installed on the device. Devices with exclusively approved applications receive the maximum score (10), ensuring compliance and minimizing security risks. If unapproved software is detected, a penalty of up to –5 points is applied within this group, reflecting potential operational, security, or policy compliance concerns.
- Only approved software installed: score 10
- Unapproved software detected: penalty of up to –5 points in this group.
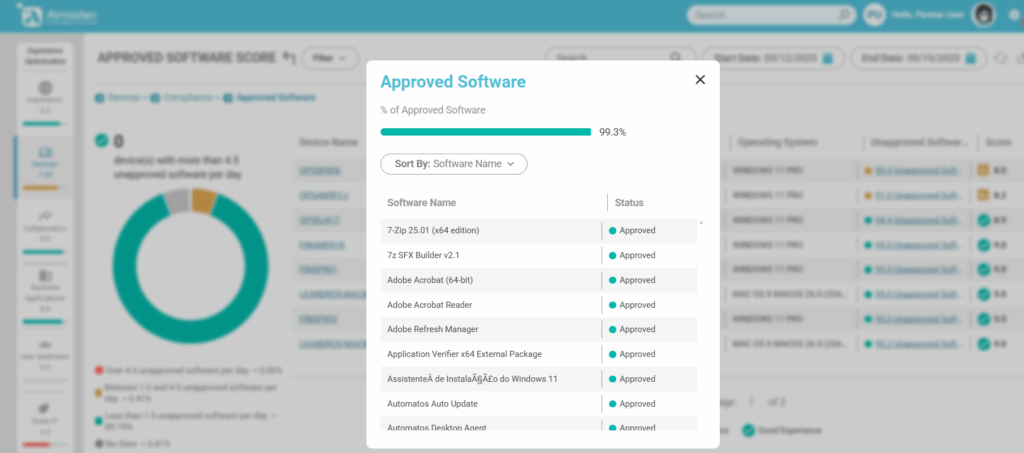
- Note: Software approval is done at CIQ ITAM.
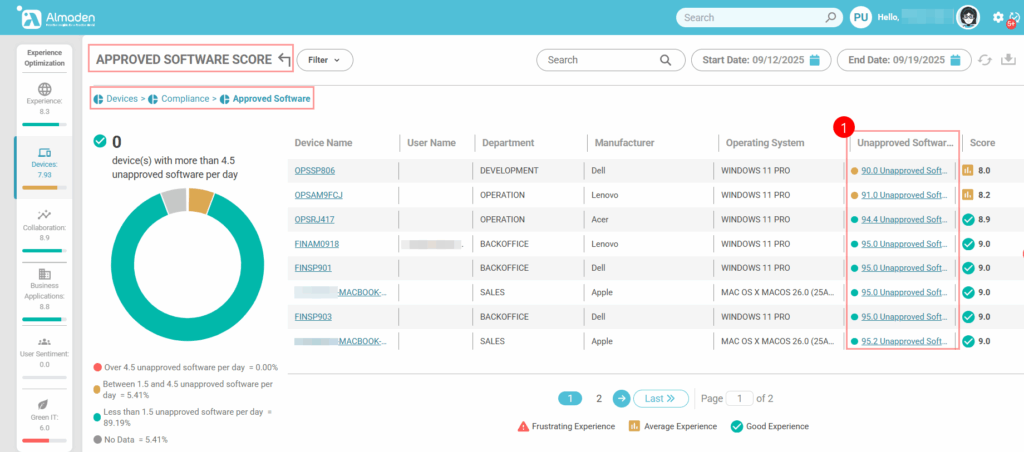
- Identify unapproved or undefined software by clicking on the “Unapproved Software” column
3. Stability and Configuration
Measures the operating system’s stability and the correctness of its internal configuration. This group evaluates factors such as system errors and WMI health to determine how reliably the device operates. A higher score reflects a stable and well-configured system, reducing unexpected crashes, failures, or disruptions that could negatively impact the user experience:
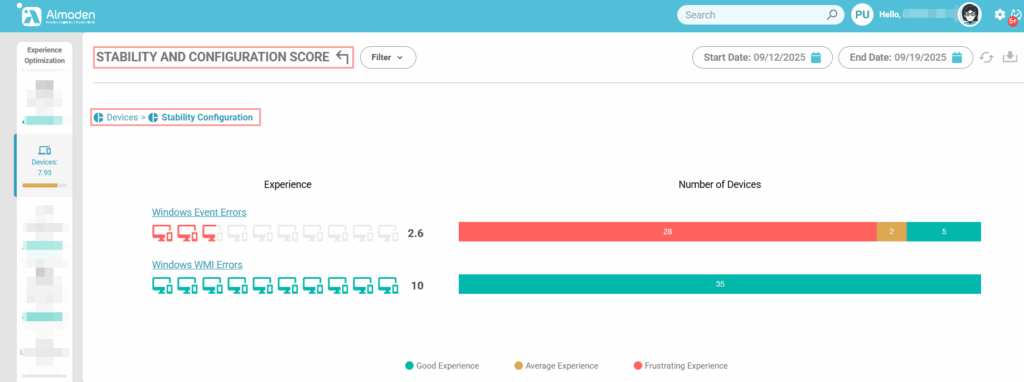
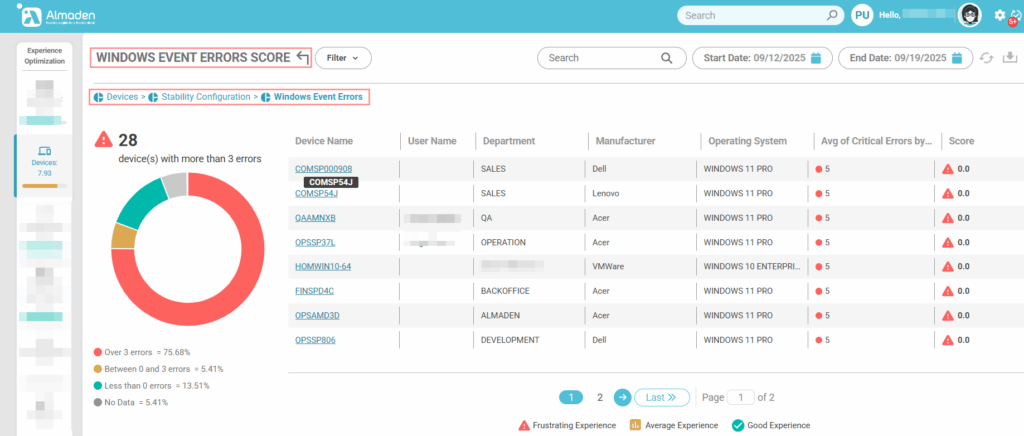
3.1 Windows Event Errors
Evaluates the number and severity of critical errors logged in the Windows Event Viewer. Devices with few or no critical errors receive the maximum score (10), indicating a stable and reliable system. Devices experiencing multiple recurring errors, such as kernel faults, driver failures, or BSODs (Blue Screen of Death), receive a reduced score (≤ 5), reflecting potential instability that can impact user productivity.
- Few or no critical errors logged: score 10
- Multiple recurring errors (Kernel, Drivers, BSOD): score ≤ 5
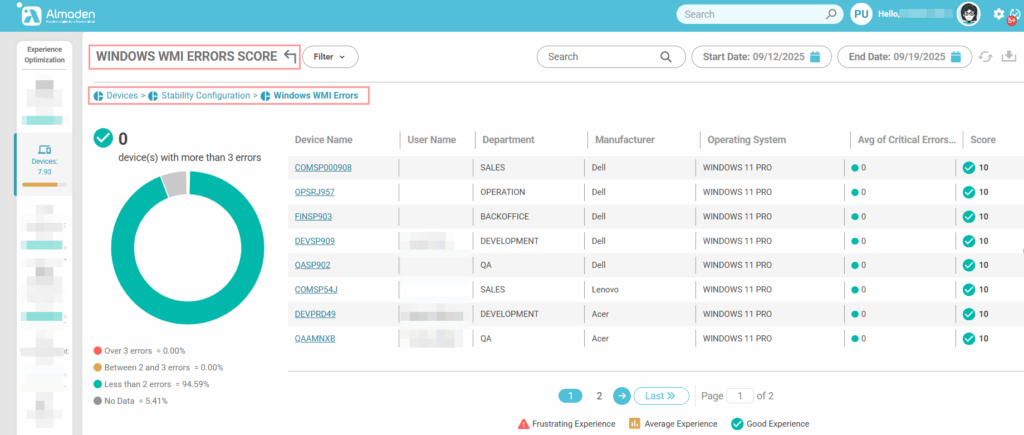
3.2 Windows WMI Errors
Assesses the health and reliability of the Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) system. A fully healthy WMI, with no errors in namespaces or queries, receives the maximum score (10), indicating that system monitoring and management functions are operating correctly. Devices with recurring namespace or query failures receive a reduced score (≤ 4), reflecting potential issues that can affect system stability and the accuracy of collected performance data.
- Healthy WMI: score 10
- Recurring namespace or query failures: score ≤ 4